The first refereed research paper with data taken on our second small-angle-scattering instrument, Bilby, has just been published on-line in Langmuir.
The collaborative work, involving National Taiwan University, Moscow State University, the Taiwanese National Synchrotron Radiation Research Center, and ANSTO, results from one of the first experiments on Bilby from our peer-reviewed proposal system.
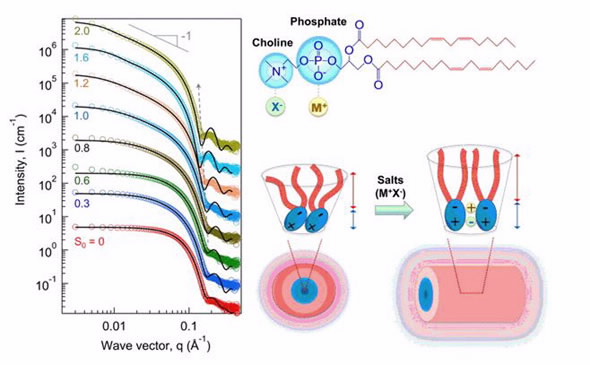
The research team used rheological techniques and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, in addition to small-angle neutron scattering, to investigate the effects of inorganic ions on the self-assembly of lecithin, a zwitterionic phosphatidylcholine, in cyclohexane. The results on lecithin organogels have implications for our understanding of the physiological process in human bodies, with potential for biomedical applications, as well as rheological control of oils.
The full reference is "Effects of Alkali Cations and Halide Anions on the Self-Assembly of Phosphatidylcholine in Oils", S.-T. Lin, C.-S. Lin, Y.-Y. Chang, A. E. Whitten, A. Sokolova, C.-M. Wu, V. A. Ivanov, A. R. Khokhlov and S.-H. Tung, Langmuir, 32(46) (2016) 12166-12174
DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b03449
Published: 23/11/2016


